# generate a synthetic dataset with known classes: 50 features, 23 samples (10+5+8)
n <- 20; counts <- c(5, 3, 2);
p <- sum(counts)
x <- syntheticNMF(n, counts)
dim(x)
[1] 20 10
# build the true cluster membership
groups <- unlist(mapply(rep, seq(counts), counts))
# run on a data.frame
res <- nmf(data.frame(x), 3)
# missing method: use algorithm suitable for seed
res <- nmf(x, 2, seed=rnmf(2, x))
algorithm(res)
[1] "brunet"
res <- nmf(x, 2, seed=rnmf(2, x, model='NMFns'))
algorithm(res)
[1] "nsNMF"
# compare some NMF algorithms (tracking the approximation error)
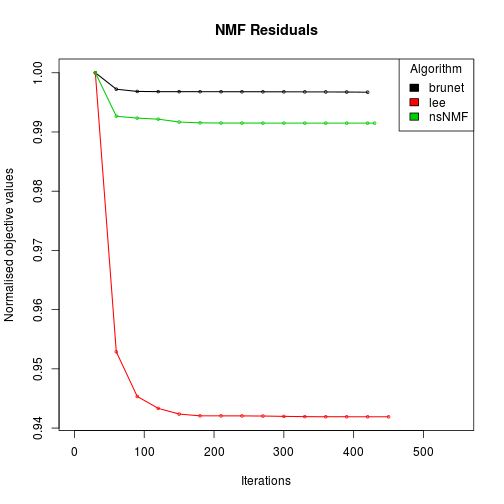
res <- nmf(x, 2, list('brunet', 'lee', 'nsNMF'), .options='t')
Compute NMF method 'brunet' [1/3] ... OK
Compute NMF method 'lee' [2/3] ... OK
Compute NMF method 'nsNMF' [3/3] ... OK
res
Length: 3
Method(s): brunet, lee, nsNMF
Total timing:
user system elapsed
1.142 0.000 1.142
summary(res, class=groups)
method seed rng metric rank sparseness.basis sparseness.coef purity entropy silhouette.coef silhouette.basis residuals niter
brunet brunet random 1 KL 2 0.2932845 0.8254661 0.7 0.4984430 1 1 67.54475 420
lee lee random 1 euclidean 2 0.3725724 0.6479075 0.8 0.3063008 1 1 40.01078 450
nsNMF nsNMF random 1 KL 2 0.3613243 0.9999992 0.7 0.4984430 1 1 71.77176 430
cpu cpu.all nrun
brunet 0.109 0.109 1
lee 0.164 0.164 1
nsNMF 0.207 0.207 1
# plot the track of the residual errors
plot(res)
# specify algorithm by its name
res <- nmf(x, 3, 'nsNMF', seed=123) # nonsmooth NMF
# names are partially matched so this also works
identical(res, nmf(x, 3, 'ns', seed=123))
[1] FALSE
res <- nmf(x, 3, 'offset') # NMF with offset
# run a custom algorithm defined as a standard function
myfun <- function(x, start, alpha){
# update starting point
# ...
basis(start) <- 3 * basis(start)
# return updated point
start
}
res <- nmf(x, 2, myfun, alpha=3)
algorithm(res)
[1] "nmf_1eff752fc498"
# error: alpha missing
try( nmf(x, 2, myfun) )
# Model:
features: 20
basis/rank: 2
samples: 10
# Details:
algorithm: nmf_1eff6a26d7ae
seed: random
RNG: 403L, 111L, ..., 905346294L [32127b1f5d128e86611ca13100c4e072]
distance metric: 'euclidean'
residuals: 93757.77
Timing:
user system elapsed
0.004 0.000 0.003
# possibly the algorithm fits a non-standard NMF model, e.g. NMFns model
res <- nmf(x, 2, myfun, alpha=3, model='NMFns')
modelname(res)
[1] "NMFns"
# assume a known NMF model compatible with the matrix `x`
y <- rnmf(3, x)
# fits an NMF model (with default method) on some data using y as a starting point
res <- nmf(x, y)
# the fit can be reproduced using the same starting point
nmf.equal(nmf(x, y), res)
[1] TRUE
# missing method: use default algorithm
res <- nmf(x, 3)
# Fit a 3-rank model providing an initial value for the basis matrix
nmf(x, rmatrix(nrow(x), 3), 'snmf/r')
# Model:
features: 20
basis/rank: 3
samples: 10
# Details:
algorithm: snmf/r
seed: NMF
RNG: 403L, 471L, ..., 905346294L [5b3bc938a22917243a2ad8c9fc79d83d]
distance metric:
residuals: 32.96566
Iterations: 70
Timing:
user system elapsed
0.160 0.000 0.164
# Fit a 3-rank model providing an initial value for the mixture coefficient matrix
nmf(x, rmatrix(3, ncol(x)), 'snmf/l')
# Model:
features: 20
basis/rank: 3
samples: 10
# Details:
algorithm: snmf/l
seed: NMF
RNG: 403L, 515L, ..., 905346294L [a4cdbeabe17bc6669787b00b08588da7]
distance metric:
residuals: 32.93398
Iterations: 65
Timing:
user system elapsed
0.151 0.000 0.151
# default fit
res <- nmf(x, 2)
summary(res, class=groups)
rank sparseness.basis sparseness.coef purity entropy silhouette.coef silhouette.basis residuals
2.0000000 0.3836735 0.6690929 0.8000000 0.3811979 1.0000000 1.0000000 66.2048250
niter cpu cpu.all nrun
450.0000000 0.1010000 0.1010000 1.0000000
# run default algorithm multiple times (only keep the best fit)
res <- nmf(x, 3, nrun=10)
# NOTE - CRAN check detected: limiting maximum number of cores [2/4]
# NOTE - CRAN check detected: limiting maximum number of cores [2/4] res
Method: brunet
Runs: 10
RNG:
407L, 735887289L, 356183078L, -363657105L, -463838236L, -682061419L, -2098846382L
Total timing:
user system elapsed
2.854 0.228 3.019
summary(res, class=groups)
rank sparseness.basis sparseness.coef purity entropy silhouette.coef
3.0000000 0.4680864 0.7657260 0.9000000 0.1738140 0.9266244
silhouette.basis residuals niter cpu cpu.all nrun
0.8109707 44.6115320 420.0000000 0.1200000 2.8540000 10.0000000
cophenetic dispersion silhouette.consensus
0.9802005 0.7080000 0.7582481
# run default algorithm multiple times keeping all the fits
res <- nmf(x, 3, nrun=10, .options='k')
# NOTE - CRAN check detected: limiting maximum number of cores [2/4]
# NOTE - CRAN check detected: limiting maximum number of cores [2/4] res
Method: brunet
Runs: 10
RNG:
407L, 1017738740L, -1532700571L, 258173410L, -924957701L, 1735077632L, 1899471617L
Total timing:
user system elapsed
4.230 0.372 2.651
Sequential timing:
user system elapsed
1.323 0.001 1.324
summary(res, class=groups)
rank sparseness.basis sparseness.coef purity entropy silhouette.coef
3.0000000 0.4681643 0.7694107 0.9000000 0.1738140 0.9071356
silhouette.basis residuals niter cpu cpu.all nrun
0.7994680 44.6115286 430.0000000 0.1150000 4.2300000 10.0000000
cophenetic dispersion silhouette.consensus
0.9847183 0.7840000 0.8386278
## Note: one could have equivalently done
# res <- nmf(V, 3, nrun=10, .options=list(keep.all=TRUE))
# use a method that fit different model
res <- nmf(x, 2, 'nsNMF')
fit(res)
features: 20
basis/rank: 2
samples: 10
theta: 0.5
# pass parameter theta to the model via `...`
res <- nmf(x, 2, 'nsNMF', theta=0.2)
fit(res)
features: 20
basis/rank: 2
samples: 10
theta: 0.2
## handling arguments in `...` and model parameters
myfun <- function(x, start, theta=100){ cat("theta in myfun=", theta, "\n\n"); start }
# no conflict: default theta
fit( nmf(x, 2, myfun) )
theta in myfun= 100
features: 20
basis/rank: 2
samples: 10
# no conlfict: theta is passed to the algorithm
fit( nmf(x, 2, myfun, theta=1) )
theta in myfun= 1
features: 20
basis/rank: 2
samples: 10
# conflict: theta is used as model parameter
fit( nmf(x, 2, myfun, model='NMFns', theta=0.1) )
theta in myfun= 100
features: 20
basis/rank: 2
samples: 10
theta: 0.1
# conflict solved: can pass different theta to model and algorithm
fit( nmf(x, 2, myfun, model=list('NMFns', theta=0.1), theta=5) )
theta in myfun= 5
features: 20
basis/rank: 2
samples: 10
theta: 0.1
## USING SEEDING METHODS
# run default algorithm with the Non-negative Double SVD seeding method ('nndsvd')
res <- nmf(x, 3, seed='nndsvd')
## Note: partial match also works
identical(res, nmf(x, 3, seed='nn'))
[1] FALSE
# run nsNMF algorithm, fixing the seed of the random number generator
res <- nmf(x, 3, 'nsNMF', seed=123456)
nmf.equal(nmf(x, 3, 'nsNMF', seed=123456), res)
[1] TRUE
# run default algorithm specifying the starting point following the NMF standard model
start.std <- nmfModel(W=matrix(0.5, n, 3), H=matrix(0.2, 3, p))
nmf(x, start.std)
# Model:
features: 20
basis/rank: 3
samples: 10
# Details:
algorithm: brunet
seed: NMF
RNG: 403L, 342L, ..., 1047588911L [8ed89da992168bfe13a600ef97943baa]
distance metric: 'KL'
residuals: 89.23127
Iterations: 420
Timing:
user system elapsed
0.092 0.000 0.092
# to run nsNMF algorithm with an explicit starting point, this one
# needs to follow the 'NMFns' model:
start.ns <- nmfModel(model='NMFns', W=matrix(0.5, n, 3), H=matrix(0.2, 3, p))
nmf(x, start.ns)
# Model:
features: 20
basis/rank: 3
samples: 10
theta: 0.5
# Details:
algorithm: nsNMF
seed: NMF
RNG: 403L, 342L, ..., 1047588911L [8ed89da992168bfe13a600ef97943baa]
distance metric: 'KL'
residuals: 70.70244
Iterations: 540
Timing:
user system elapsed
0.245 0.000 0.244
# Note: the method name does not need to be specified as it is infered from the
# when there is only one algorithm defined for the model.
# if the model is not appropriate (as defined by the algorihtm) an error is thrown
# [cf. the standard model doesn't include a smoothing parameter used in nsNMF]
try( nmf(x, start.std, method='nsNMF') )
## Callback functions
# Pass a callback function to only save summary measure of each run
res <- nmf(x, 3, nrun=3, .callback=summary)
# NOTE - CRAN check detected: limiting maximum number of cores [2/4]
# NOTE - CRAN check detected: limiting maximum number of cores [2/4] # the callback results are simplified into a matrix
res$.callback
[,1] [,2] [,3]
rank 3.0000000 3.0000000 3.0000000
sparseness.basis 0.4690227 0.4646504 0.4580022
sparseness.coef 0.8045101 0.7769446 0.8068001
silhouette.coef 0.9546248 0.8902991 0.8762803
silhouette.basis 0.8394310 0.7919504 0.7687868
residuals 44.6117396 44.6136628 45.3878071
niter 450.0000000 430.0000000 860.0000000
cpu 0.1150000 0.1080000 0.1870000
cpu.all 0.1150000 0.1080000 0.1870000
nrun 1.0000000 1.0000000 1.0000000
res <- nmf(x, 3, nrun=3, .callback=summary, .opt='-S')
# NOTE - CRAN check detected: limiting maximum number of cores [2/4]
# NOTE - CRAN check detected: limiting maximum number of cores [2/4] # the callback results are simplified into a matrix
res$.callback
[[1]]
rank sparseness.basis sparseness.coef silhouette.coef silhouette.basis residuals niter cpu
3.0000000 0.3608160 0.8514485 0.9150132 0.7120422 50.4900252 480.0000000 0.1220000
cpu.all nrun
0.1220000 1.0000000
[[2]]
rank sparseness.basis sparseness.coef silhouette.coef silhouette.basis residuals niter cpu
3.0000000 0.4684599 0.7880077 0.9424514 0.8147630 44.6115438 420.0000000 0.1080000
cpu.all nrun
0.1080000 1.0000000
[[3]]
rank sparseness.basis sparseness.coef silhouette.coef silhouette.basis residuals niter cpu
3.0000000 0.4649104 0.8032040 0.9475480 0.8329278 44.6134353 440.0000000 0.1050000
cpu.all nrun
0.1050000 1.0000000
# Pass a custom callback function
cb <- function(obj, i){ if( i %% 2 ) sparseness(obj) >= 0.5 }
res <- nmf(x, 3, nrun=3, .callback=cb)
# NOTE - CRAN check detected: limiting maximum number of cores [2/4]
# NOTE - CRAN check detected: limiting maximum number of cores [2/4] res$.callback
[[1]]
basis coef
FALSE TRUE
[[2]]
NULL
[[3]]
basis coef
FALSE TRUE
# Passs a callback function which throws an error
cb <- function(){ i<-0; function(object){ i <<- i+1; if( i == 1 ) stop('SOME BIG ERROR'); summary(object) }}
res <- nmf(x, 3, nrun=3, .callback=cb())
# NOTE - CRAN check detected: limiting maximum number of cores [2/4]
# NOTE - CRAN check detected: limiting maximum number of cores [2/4]
Warning message:
NMF::nmf - All NMF fits were successful but 2/3 callback call(s) threw an error.
# Callback error(s) thrown:
- run #1: SOME BIG ERROR
## PARALLEL COMPUTATIONS
# try using 3 cores, but use sequential if not possible
res <- nmf(x, 3, nrun=3, .options='p3')
# NOTE - CRAN check detected: limiting maximum number of cores [2/4]
# force using 3 cores, error if not possible
res <- nmf(x, 3, nrun=3, .options='P3')
# NOTE - CRAN check detected: limiting maximum number of cores [2/4]
Error: Parallel computation aborted: only 2 core(s) available [requested 3 core(s)]
# use externally defined cluster
library(parallel)
cl <- makeCluster(6)
res <- nmf(x, 3, nrun=3, .pbackend=cl)
# NOTE - CRAN check detected: limiting maximum number of cores [2/4]
# NOTE - CRAN check detected: limiting maximum number of cores [2/4]
# use externally registered backend
registerDoParallel(cl)
res <- nmf(x, 3, nrun=3, .pbackend=NULL)